High School Chemistry Resources
Visual simulations for teaching science to high school students
-
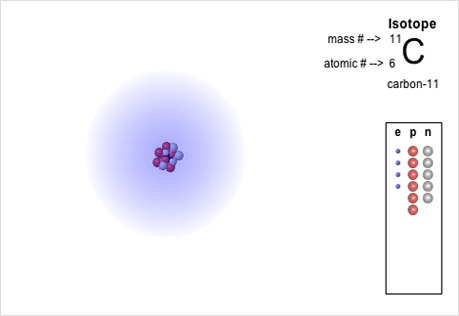
Atomic Structure
Explore ion formation, isotopes, and electron orbital placement using interactive models of atomic structure.
-
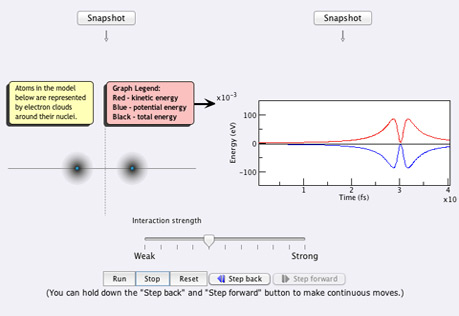
Atoms & Conservation
of EnergyHow does the Law of Conservation of Energy (the First Law of Thermodynamics) apply to atoms?
-

Baggie Chemistry
Household chemicals mixed in a baggie produce dramatic results.
Boiling Point
This model allows you to explore why polar and non-polar substances have very different boiling points.
Catalysts
Explore the effects of homogeneous catalysts.
Build Your Own Collection of Resources
Create a free account and collect the resources you want to use with your students in one location for easy access.
Create Account
Ceramic Forces
Explore what happens when a force is exerted on a ceramic material.
Charged & Neutral Atoms
Explore the role of charge in interatomic interactions.
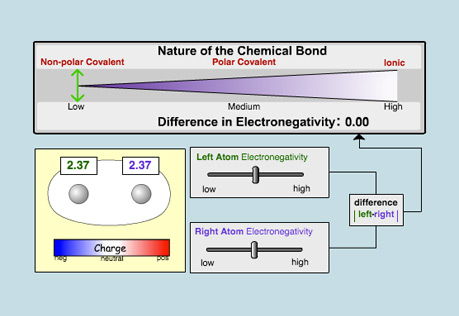
Chemical Bonds
Explore the different kinds of chemical bonds that can form, ranging from non-polar covalent to ionic.
Chemical Reactions & Stoichiometry
Change the ratios of chemicals and observe the effects to learn how to balance chemical equations.
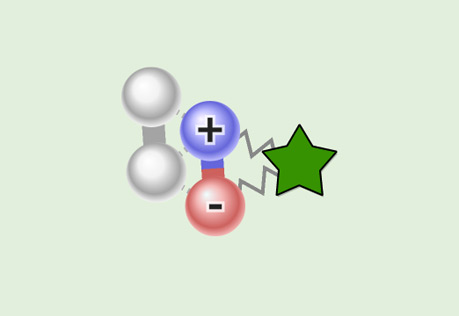
Comparing Dipole-Dipole to London Dispersion
Investigate the difference in the attractive force between polar and non-polar molecules.
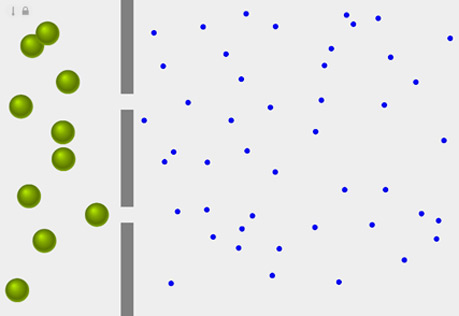
Diffusion Across a Semipermeable Membrane
Explore the role of pore size in the diffusion of a substance across a membrane.
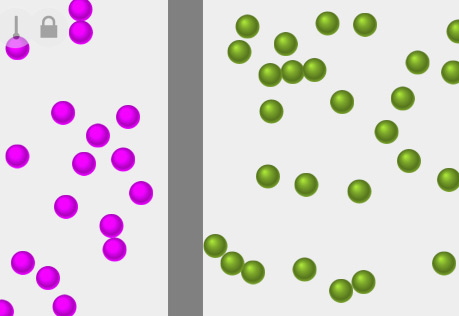
Diffusion & Molecular Mass
Explore the role of a molecule's mass with respect to its diffusion rate.
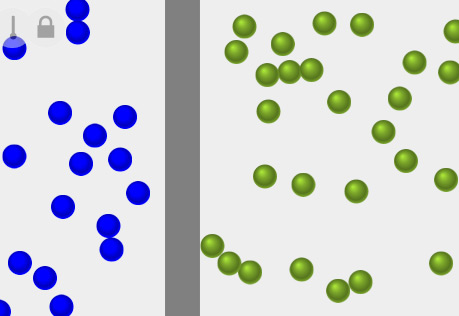
Diffusion & Temperature
Explore the role of temperature in the rate of diffusion of a substance.
Diffusion of a Drop
Explore the random molecular motion of a dye in water.
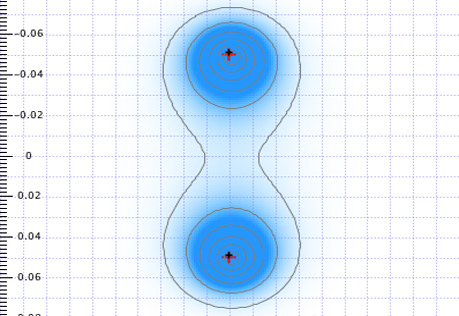
Electrons in Atoms & Molecules
The interactions of electrons with matter are central to many technologies.
Factors Affecting London Dispersion Attractions
Explore the role of size and shape in the strength of London dispersion attractions.
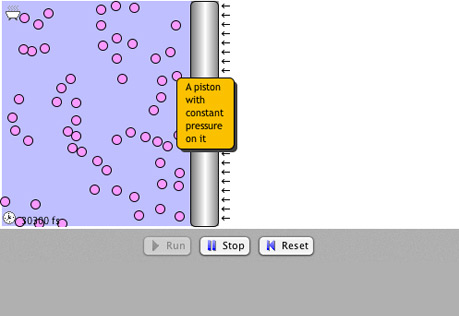
Gas Laws
Explore the interrelationships of pressure, temperature and volume with atomic models.
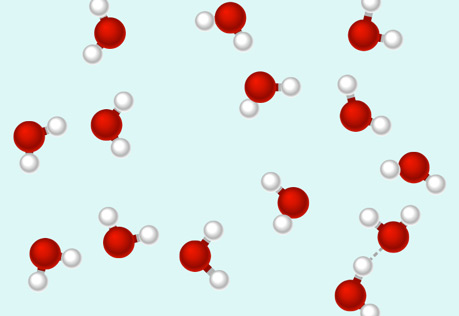
Hydrogen Bonds: A Special Type of Attraction
Explore the polar molecule interactions known as hydrogen bonds.
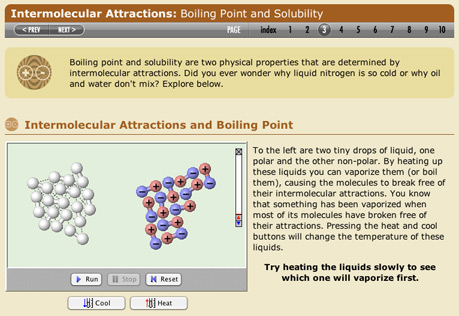
Intermolecular Attractions
Explore how London dispersion attraction and dipole-dipole interactions explain the different boiling points of materials.
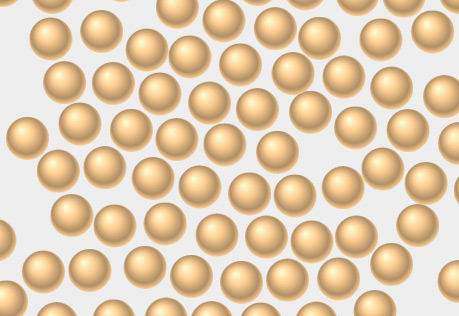
Intermolecular Attractions & States of Matter
Explore how states of matter are related to the strength of intermolecular attractions.
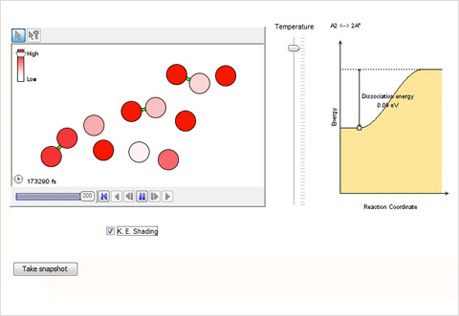
Making & Breaking Bonds
Explore the association and dissociation of diatomic molecules.
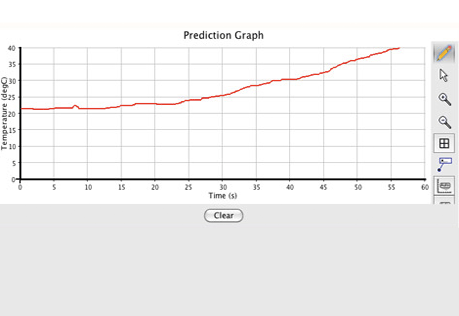
Making Heat
Does change in concentration change the amount of heat released in a chemical reaction?
Metal Forces
Explore what happens when a force is exerted on a metallic material.
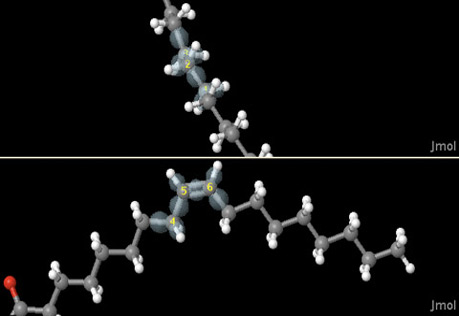
Molecular Geometry
Use models of electron arrangement around atoms to discover how molecules form linear, trigonal planar, and trigonal pyramidal shapes.
Molecular View of a Gas
Explore the structure of a gas at the molecular level.
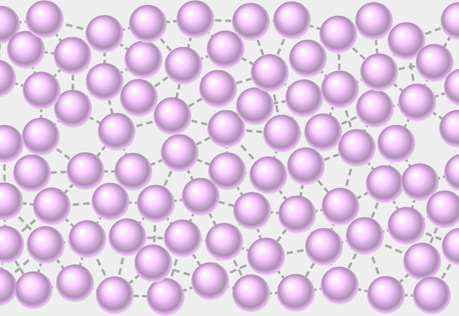
Molecular View of a Liquid
Explore the structure of a liquid at the molecular level.
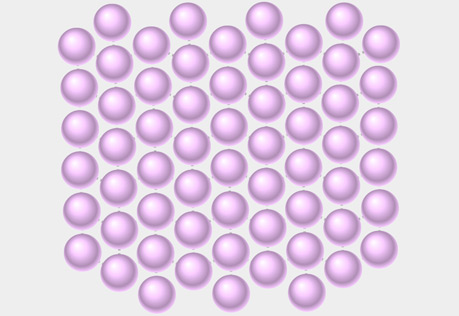
Molecular View of a Solid
Explore the structure of a solid at the molecular level.
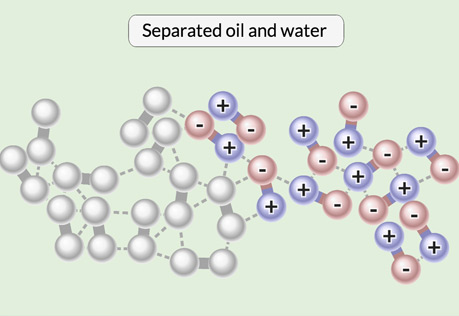
Oil & Water
Explore the interactions that cause water and oil to separate from a mixture.
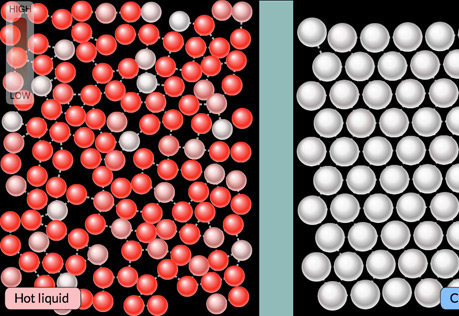
Phase Change
Explore what happens at the molecular level during a phase change.
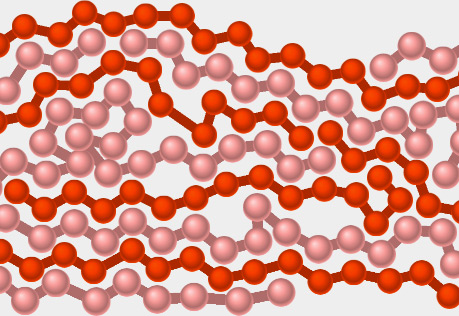
Plastic Forces
Explore what happens when a force is exerted on a polymeric plastic material.
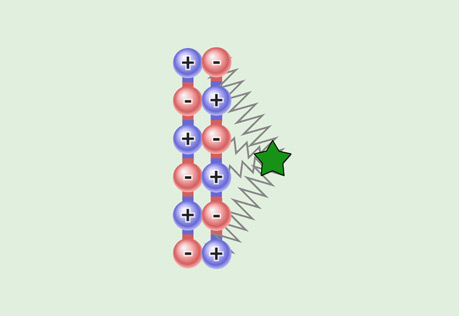
Polarity & Attractive Strength
Explore the role of polarity in the strength of intermolecular attractions.
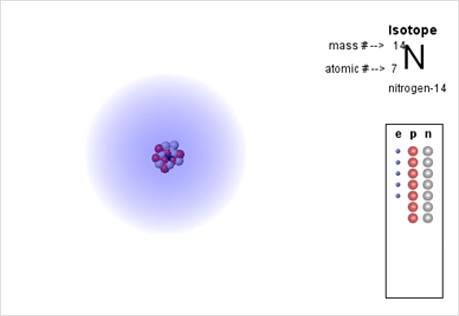
Probability Clouds
Investigate the probability map of electron orbitals.
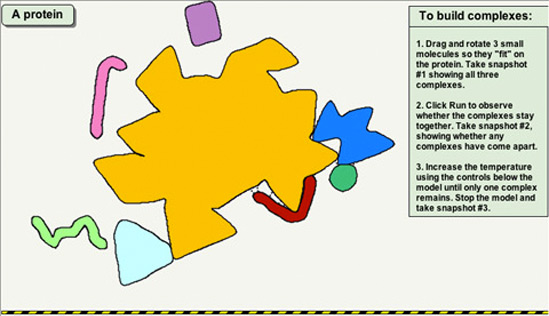
Protein Partnering & Function
Build "partnerships" between a protein and small molecules. Explore the effects of surface charge, polarity and shape.
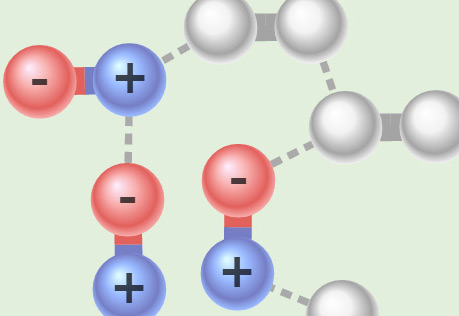
Seeing Intermolecular Attractions
Explore different types of attractions between molecules.
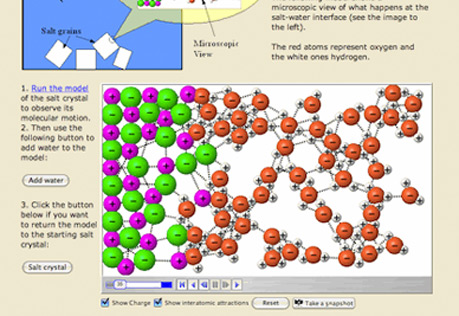
Solubility
Explore molecular views of solvents and solutes to explain how substances dissolve.
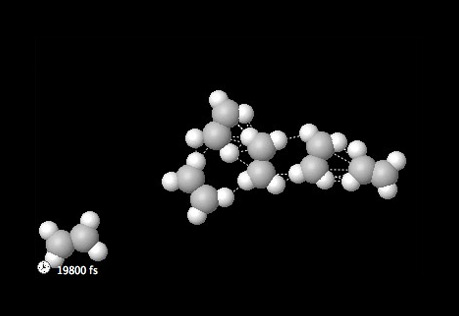
States of Matter
How do the forces and attractions differ between the states of matter?
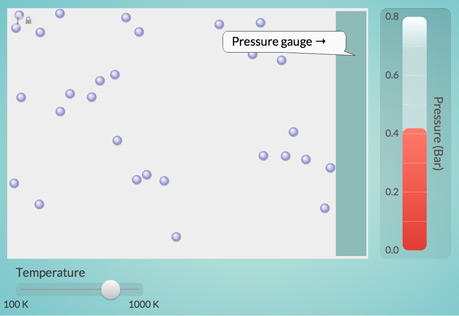
The Temperature-Pressure Relationship
Explore the relationship between the temperature of a gas and the pressure it exerts on its container.
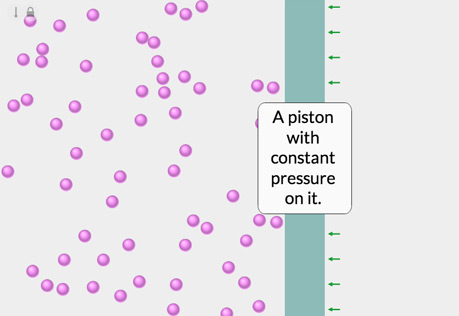
The Temperature-Volume Relationship
Explore the relationship between the temperature of a gas and its volume.

The Volume-Pressure Relationship
Investigate the relationship between the volume of a gas and the pressure it exerts on its container.
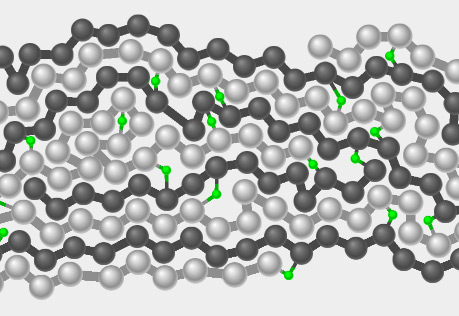
Tire Forces
Explore what happens when a force is exerted on a rubber tire.

Tree of Life
Zoom down from what we can see with our own eyes to the macromolecules from which they are made.
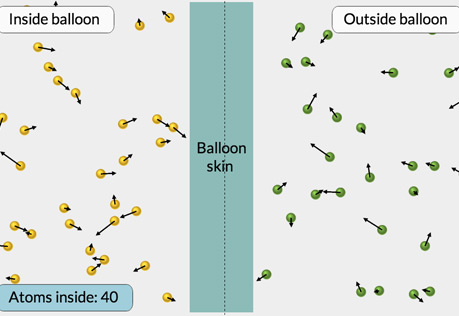
What is Pressure?
Explore pressure at the atomic level.
“Wish I learned science this way—far more interesting than reading chapters in a book.”
